Thread란 single running process를 위한 새로운 abstraction이다.
Multi-threaded program
- Multi-threaded program은 한 개 이상의 execution을 가진다.
- Multiple PCs (Program Counter)
- Thread들끼리 같은 address space를 공유한다.
각각의 thread들은 고유의 PC(Program Counter)와 register들을 가지고 있다.
- 여러개의 TCB(thread control block)이 각각의 thread의 상태를 저장하기 위해 필요하다.
만약 T1에서 T2로 switching된다면 T1의 register state는 저장이되고 T2의 register state가 restore될 것이다.
addresss space 는 같다.

thread들끼리 사용하는 address space는 같지만 그 안에서 stack영역은 따로 사용한다. (Heap과 Program Code는 공유)
Why Use Threads?
Parallelism
- Single-threaded program : task is straightforward, but slow
- Mulit-threaded program : natural and typical way to make programs run faster on modern hardware.
- Parallelization : single-threaded program을 multiple CPU 환경에서 돌아가도록 바꿔주는 것
Avoid blocking program progress due to slow I/O
- Threading enables overlap of I/O with other activities within a single program.
- It is much like multiprogramming did for processes acrosss programs.
Simple Thread Creation Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *mythread(void *arg){
printf("%s\n", (char *)arg);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
pthread_t p1, p2;
int rc;
printf("main: begin\n");
pthread_create(&p1, NULL, mythread, "A");
pthread_create(&p2, NULL, mythread, "B");
// join waits for the threads to finish
pthread_join(p1, NULL);
pthread_join(p2, NULL);
printf("main: end\n");
return 0;
}
위의 코드는 deterministic하게 돌아가는 것이아니라 다음처럼 여러가지 경우의 수로 돌아간다.



Race condition
Race condition이란 결과값이 실행 timing에 걸린 것을 의미한다.( nondeterministic 하다 )
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
static volatile int counter = 0;
void *mythread(void* arg){
printf("%s: begin\n", (char *)arg);
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 1e7; i++)
counter = counter + 1;
printf("%s: done\n", (char *)arg);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
pthread_t p1, p2;
int rc;
printf("main: begin (counter = %d)\n", counter);
pthread_create(&p1, NULL, mythread, "A");
pthread_create(&p2, NULL, mythread, "B");
// join waits for the threads to finish
pthread_join(p1, NULL);
pthread_join(p2, NULL);
printf("main: done with both (counter = %d)\n", counter);
return 0;
}위에 코드를 실행시키면 counter의 같은 2,000,000값이 나올것 같지만 절대 그렇게 나오지 않는다.
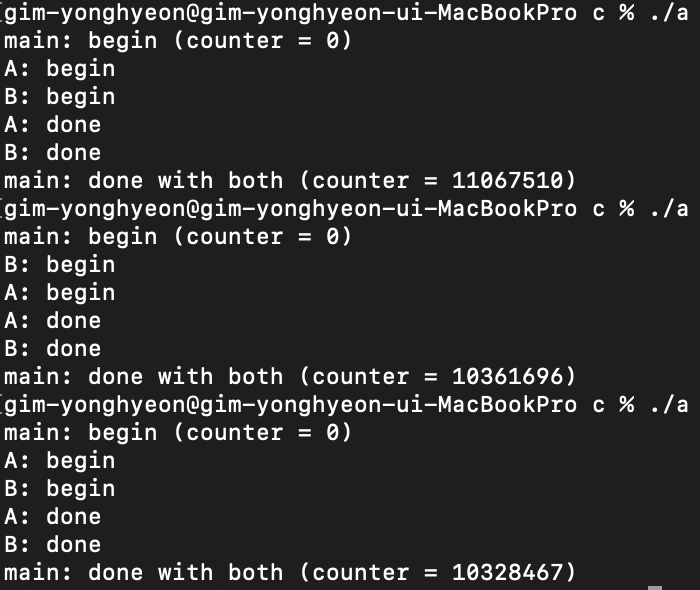
그 이유는 counter 값이 %eax에 저장되기 전에 interrput가 걸리고 변형되지 않은 counter값을 다시 불러왔기 때문이다.
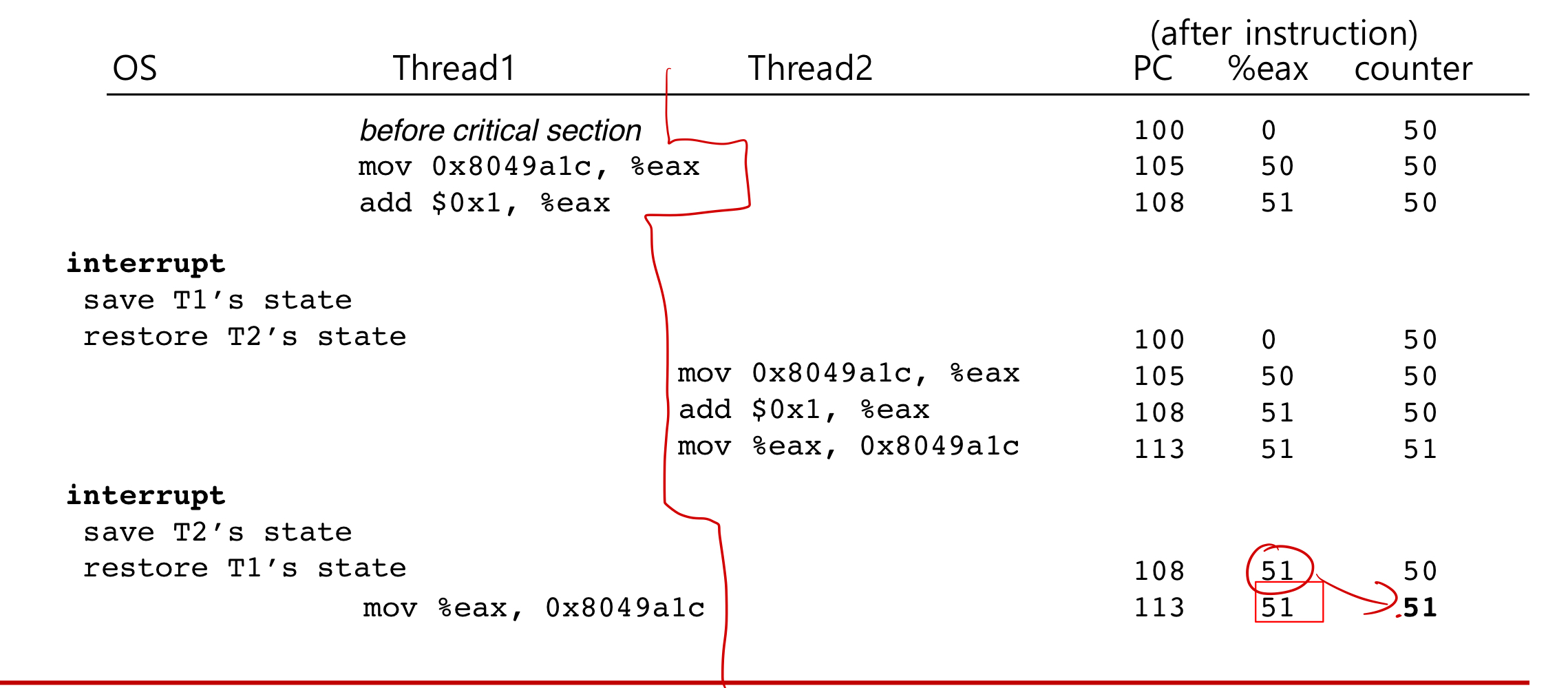
따라서 Race condition을 없애기 위해서는 Critical section을 읽고 있을 때, lock을 사용하여 interrupt가 걸리지 못하게 해주어야 한다.

'3-2 > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Locks (0) | 2021.11.12 |
|---|---|
| Thread API (0) | 2021.11.08 |
| LRU Implementation in more detail (0) | 2021.11.08 |
| Swapping Policies (0) | 2021.11.08 |
| Swapping Mechanisms (0) | 2021.11.08 |